Contrary to popular belief, humans are not spread across the surface evenly. The world's population as a whole, or the global distribution, is concentrated in a few places. Human beings tend to avoid the parts of the Earth they contend to be too wet, too dry, too cold, or too mountainous. In other words, we like living on the Earth where we seem to like according to our senses. The capacity of Earth to support a much larger population depends greatly on people's ability to use sparsely settled lands more effectively.
Population concentrations are clustered in four distinct regions- East Asia, South Asia, Southeast Asia, and Western Europe. These population clusters have some similarities. They are all near large sources of water. An ocean or river is in close proximity with large population centers. Population concentrations can occur for a wide variety of number reasons. As seen in this population cartogram, population clusters occur with easy access to natural resources and water. (Fig. 1)
- East Asia- One fifth of the world's population live in just East Asia. The region is located on the border of the Pacific Ocean and includes Eastern China, Japan, Korea (both), and Taiwan. Most of the population is attributed to the People's Republic of China. (It is the world's 3rd largest country in land area.) Most of the Chinese leave near the Pacific Ocean or near the river valleys of the Huang or Yangtze. In Japan and Korea, population is clustered in metropolitan area. Unlike China, most of their citizens live urban lifestyles.
- South Asia- Another fifth of the world population live in South Asia alone. This area includes India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka. The most important concentration of people live along a 900 mile corridor from Lahore, Pakistan through India to the Bay of Bengal. Population is also concentrated along India's two coasts.Like China, most people work as farmers. (Only a fourth work in urban areas.)
- Southeast Asia- This is the fourth largest population cluster. A half-billion people live across the a series of islands that spread from the Indian Ocean to the Pacific. The largest concentration is on Java. Indonesia is the fourth most populous country. Like China and India, most of its citizenry are farmers and live in rural areas.
- Europe- After combining all the parts that make up Europe as a whole, you have formed the third largest population cluster in the world. This is 1/9th of the world's total people. The region is unique because of the size range of the countries from Monaco to Russia. In contrast to the Asian population clusters, 75% of Europe's population are involved in city life as workers. Europe also has many more roads and railroads that connect the country. Although Europeans have decent weather for crops, they must import for the majority of their food supply.
- Eastern North America- This cluster, which extends from the Atlantic coast to the southeastern part of Canada, is the largest cluster in the Western Hemisphere. About 2% of the world's population live in this area. They are most like Europeans and dwell in cities. This includes the cities such as Boston and Newport News, Virginia.
Sparsely populated regions on the other hand include land that is too dry. Deserts and low precipitation average countries can very easily drive people away. This is due to the fact that they cannot supply the one necessity every living thing needs; water. Dry lands include the countries near the Sahara, Siberia, and the Gobi desert. Wet lands also drive people away due to the fact that lands that receive too much rain tend to be inhospitable.
 |
| Figure 2: Mexico City |
- Dry Lands- These lands, which encompass about 20% of the Earth's surface, are areas that are too dry for farming. The two largest desert regions in the world (in the North Hemisphere) are between 15 and 50 degrees north latitude and (in the South Hemisphere) between 20 and 50 degrees south latitude. The largest desert region is the Saharan belt. This is made up of the Sahara, Arabian, Thar, Takla Makan, and Gobi deserts. These are sparse areas because they lack the water to grow crops. They are now being revisited in an effort to locate new resources such as oil.
- Wet Lands- These are lands that receive high amount of precipitation. These lands are mostly near the Equator. They are characteristically very warm and humid as well. Because average rainfall is so much, these lands are inhospitable to many, killing crops just as bad as drought. In India, high precipitation can be seasonal like the Monsoon season.
- Cold Lands- These are lands near the North and South poles that are perpetually covered by snow. No sane human would choose to live in this frigid wasteland. The polar regions receive less rain than even deserts. Few animals even live in these places.
- High Lands- Few people live in high areas. High mountains are treacherous, snow covered, and unsuitable for agriculture. Switzerland has less than 5% of its population in the Alps. Exceptions include places in South America where people prefer to live in higher places. One of world's largest city, Mexico City, is located at 7,360 feet high. (Fig. 2)
Population density covers the wide range of comparing people to a feature involved in geography. Population density can be identified in a number of ways including arithmetic density, physiological density, and agricultural density. Each of these measures are designed to show key aspects of different kinds of countries. (The United States and Rwanda will have dramatically different population density measures.)
The world's population is distributed unevenly across the surface. It is heavily concentrated where there is access to water and resources. It less populated in areas that are deemed inhospitable. We can measure the populations distribution by means of population density indicators.
Current Events in Population Distribution
Key Issue #1 Event Article
Australian colleges are now becoming more decentralized as time progresses. This is caused by the fact that Australia's ecumene is changing so that it is becoming slightly larger and spreading more and more each year. Professor Hugo, an expert demographer, says that Australia's traditional very regional school system as a whole is much too centralized. He sites the fact that over the past 30 years, more and more of Australia's universities are reaching capacity and have too many students. Eventually, within the next 50 years, overpopulation in the current tertiary schooling system will cause a decentralization of schools over a larger portion of Australia. A major part is the population distribution. A large part of the population of Australia live near the coasts facing Pacific. With new resources, more Australians are moving from major centers like Syndney and Perth to cities on other coasts. (See fig 4) In sum, this article illustrates an example of where population was distributed in Australia and how it is changing.
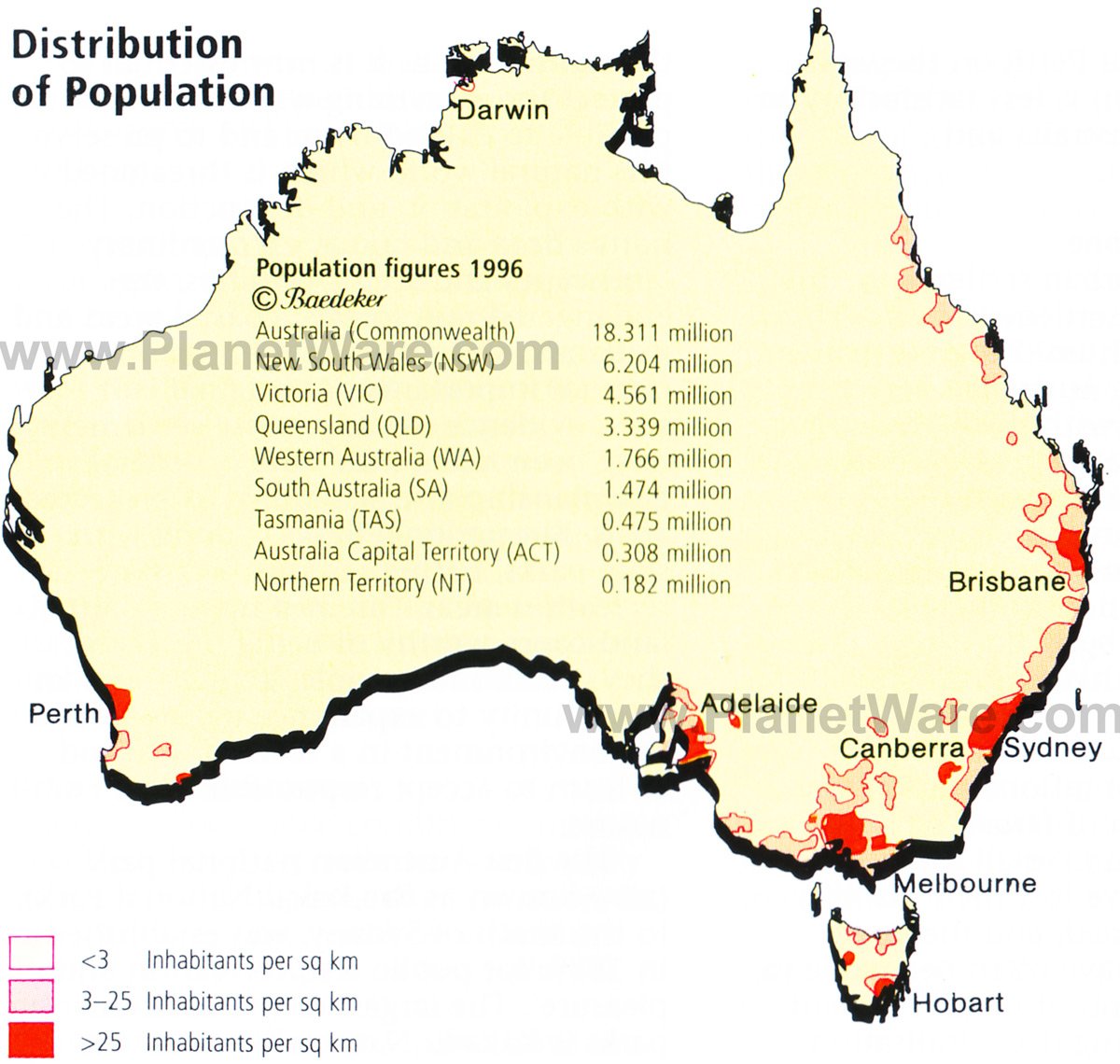 |
| Figure 4: Australia, lads |
Key Words
- Demography- study of human population
- Globalization- the growing interconnectedness of the world by means of advanced telecommunications and business practices that are bringing humans and ideas closer
- Overpopulation- people exceed the food production and the world cannot support them
- Ecumene- portion of Earth that is occupied by permanent human settlement
- Arithmetic density- number of people divided by total land area
- Physiological density- number of people supported an area of arable land (farmable) (fig. 3)
- Agricultural density- number of farmers to arable land
 |
| Figure 3: Physiological density |
